The simplest definition of risk is the probability an incident occurs times the impact of the incident. The higher this number is, the higher the risk. With the identification of risk then comes the method of how to handle risk. The four risk management strategies are mitigation, transference, avoidance and acceptance. Three of these strategies can be utilized by a company that finds itself in the later stages of the Technology Adoption Life Cycle, where they have a solid customer base that is looking for stability. However, only mitigation works for companies that are attempting to enter the market and capture the Innovators and Early Adopters.
What are the Risk Management Strategies?
The four strategies mentioned are:
- Mitigation: Knowing an incident is going to occur and attempting to minimize its impact or probability.
- Transference: Transferring the burden of the risk to someone else. Usually done through insurance.
- Avoidance: Not doing an activity, thereby eliminating the probability of the incident occurring.
- Acceptance: Realizing that you have done all you can and must accept both the impact and the probability of an incident.
Handling Risk
As stated earlier, for new products to the market, the most viable option of managing risk is through mitigation. If a company was to avoid the risk, then that would potentially deprecate the product they were trying to bring to market. By transferring a company runs the risk of losing its early customer base when an incident occurs, likewise with accepting the risk.
So how can you handle the risk as a company attempting to attract Innovators and Early Adopters? The answer is in using the AKF Risk Model.
AKF and Risk
In his article, Evaluating Technology Risk Using Mathematics, Geoffrey Weber lays out a finite method of identifying a certain level of risk a company may be at utilizing impact, probability and the ability to detect. This method returns concrete data that would then allow a company to prioritize what risk they intended to manage.
Once you have prioritized your risk and are now determining how to mitigate it, the five main components to the AKF Risk Model can be used. Depending on whether impact or probability was the issue, the below areas can be focused on to mitigate the overall risk.
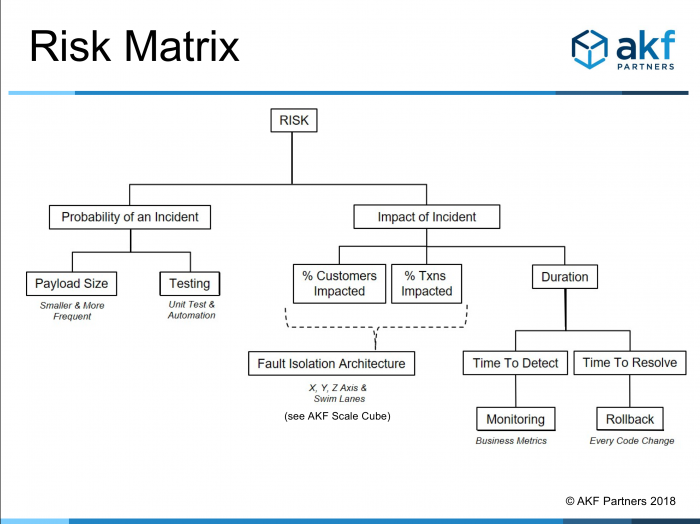
How to Affect Probability
- Payload Size: By limiting the sizes of change that are introduced to a product, the probability of an incident occurring is limited. This ensures that if an incident occurs it only affects a small aspect of the product.
- Testing: Testing aims to mitigate potential incidents prior to them occurring. Unit testing and code review will not catch 100% of the issues that may arise, but it helps to lessen the probability that something was to occur.
How to Affect Impact
- Fault Isolation Architecture: By utilizing the AKF Scale Cube, Fault Isolation will be built into the product. This helps to mitigate the impact of an incident to just a small percentage of the overall customer base.
- Monitoring: The establishment of proper monitoring provides developers a way to identify issues just prior to occurring, or as they occur. With real-time monitoring an incident can be identified as it is occurring and the company can quickly act to mitigate the impact.
- Rollback: If an incident has occurred, being able to rollback the product helps to lessen the impact. If a stable version of the product exists then that can be implemented while the company identifies what happened with the newer deployment, allowing customers to continue with their interactions.
Where does your company fit in?
If you find yourself with a customer base of Laggards and Late Majority then you have a lot more options for managing risk. Issues that arise through the use of transference, acceptance and avoidance still allow you to maintain solid sales.
If you find yourself with a customer base of Innovators and Early Adopters then you have less options for managing risk. Mitigation is the most beneficial option that is available to you for you to continue to move through the cycle and start to pick up the Early Majority.
If the AKF Risk Model is something you would like to learn more about, feel free to reach out to AKF.